Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Hattori, Koichi*; Suenaga, Daiki*; Suzuki, Kei; Yasui, Shigehiro*
Physical Review B, 108(24), p.245110_1 - 245110_11, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We develop a mean-field theory of a novel Kondo effect emerging in systems without a Fermi surface, which instead emerges under strong magnetic fields. We determine the magnitude of the Kondo condensate, which is a particle pairing composed of conducting Dirac fermions and localized impurities. We focus on the competition between the Kondo effect and the energy gap formation that stems from the pairing among the Dirac fermions leading to the dynamical chiral symmetry breaking. We find that this competition induces a quantum critical point. We also investigate finite-temperature effects. This system at vanishing fermion density can be studied with Monte Carlo lattice simulations, which do not suffer from the sign problem.
Kim, Y.*; Oka, Makoto; Suenaga, Daiki*; Suzuki, Kei
Physical Review D, 107(7), p.074015_1 - 074015_15, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:54.75(Astronomy & Astrophysics)A chiral effective theory of scalar and vector diquarks is formulated, which is based on 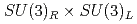 chiral symmetry and includes interactions between scalar and vector diquarks with one or two mesons. We find that the diquark interaction term with two mesons breaks the
chiral symmetry and includes interactions between scalar and vector diquarks with one or two mesons. We find that the diquark interaction term with two mesons breaks the 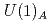 and flavor
and flavor 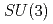 symmetries. To determine the coupling constants of the interaction Lagrangians, we investigate one-pion emission decays of singly heavy baryons
symmetries. To determine the coupling constants of the interaction Lagrangians, we investigate one-pion emission decays of singly heavy baryons 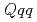 (
(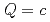 ,
,  and
and 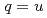 ,
,  ,
,  ), where baryons are regarded as diquark-heavy-quark two-body systems. Using this model, we present predictions of the unobserved decay widths of singly heavy baryons. We also study the change of masses and strong decay widths of singly heavy baryons under partial restoration of chiral symmetry.
), where baryons are regarded as diquark-heavy-quark two-body systems. Using this model, we present predictions of the unobserved decay widths of singly heavy baryons. We also study the change of masses and strong decay widths of singly heavy baryons under partial restoration of chiral symmetry.
Hattori, Koichi*; Suenaga, Daiki*; Suzuki, Kei; Yasui, Shigehiro*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 276, p.01015_1 - 01015_5, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.91(Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical)We investigate the QCD phase diagram in strong magnetic fields with heavy-quark impurities and determine the ground state within the mean-field analysis. The ground state is characterized by magnitudes of the pairing not only between the light quark and antiquark, i.e., chiral condensate, but also between the light quark and heavy-quark impurity, dubbed the Kondo condensate. We propose signatures of the interplay and/or competition between those two pairing phenomena reflected in the magnitude of the chiral condensate that is saturated with respect to the magnetic-field strength and anomalously increases with increasing temperature.
Suenaga, Daiki*; Araki, Yasufumi; Suzuki, Kei; Yasui, Shigehiro*
Physical Review D, 105(7), p.074028_1 - 074028_19, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:36.77(Astronomy & Astrophysics)We propose a new mechanism of the heavy-quark spin polarization (HQSP) in quark matter induced by the Kondo effect under an external magnetic field. The Kondo effect is caused by a condensate between a heavy and a light quark called the Kondo condensate leading to a mixing of the heavy- and light-quark spins. Thus, the HQSP is driven through the Kondo effect from light quarks coupling with the magnetic field in quark matter. For demonstration, we employ the Nambu-Jona-Lasinio type model under a magnetic field and investigate the HQSP within the linear response theory with vertex corrections required by the 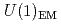 electromagnetic gauge invariance. As a result, we find that the HQSP arises significantly with the appearance of the Kondo effect. Our findings are testable in future sign-problem-free lattice simulations.
electromagnetic gauge invariance. As a result, we find that the HQSP arises significantly with the appearance of the Kondo effect. Our findings are testable in future sign-problem-free lattice simulations.
Kim, Y.*; Oka, Makoto; Suzuki, Kei
Physical Review D, 105(7), p.074021_1 - 074021_17, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:93.15(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Energy spectrum of doubly heavy tetraquarks, 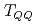 (
(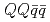 with
with 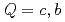 and
and 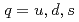 ), is studied in the potential chiral-diquark model. Using the chiral effective theory of diquarks and the quark-diquark-based potential model, the
), is studied in the potential chiral-diquark model. Using the chiral effective theory of diquarks and the quark-diquark-based potential model, the 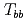 ,
, 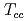 , and
, and 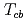 tetraquarks are described as a three-body system composed of two heavy quarks and an antidiquark. We find several
tetraquarks are described as a three-body system composed of two heavy quarks and an antidiquark. We find several 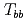 bound states, while no
bound states, while no 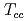 and
and 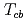 (deep) bound state is seen. We also study the change of the
(deep) bound state is seen. We also study the change of the 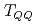 tetraquark masses under restoration of chiral symmetry.
tetraquark masses under restoration of chiral symmetry.
Meng, Q.*; Harada, Masayasu*; Hiyama, Emiko; Hosaka, Atsushi; Oka, Makoto
Physics Letters B, 824, p.136800_1 - 136800_5, 2022/01
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:97.23(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Spectrum of the doubly heavy tetraquarks, 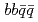 , is studied in a constituent quark model. Four-body problem is solved in a variational method where the real scaling technique is used to identify resonant states above the fall-apart decay thresholds. In addition to the two bound states that were reported in the previous study we have found several narrow resonant states above the
, is studied in a constituent quark model. Four-body problem is solved in a variational method where the real scaling technique is used to identify resonant states above the fall-apart decay thresholds. In addition to the two bound states that were reported in the previous study we have found several narrow resonant states above the 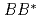 and
and 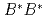 thresholds. Their structures are studied and are interpreted by the quark dynamics. A narrow resonance with spin-parity
thresholds. Their structures are studied and are interpreted by the quark dynamics. A narrow resonance with spin-parity 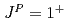 is found to be a mixed state of a compact tetraquark and a
is found to be a mixed state of a compact tetraquark and a 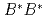 scattering state. This is driven by a strong color Coulombic attraction between the
scattering state. This is driven by a strong color Coulombic attraction between the 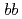 quarks. Negative-parity excited resonances with
quarks. Negative-parity excited resonances with 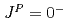 ,
, 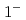 and
and 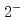 form a triplet under the heavy-quark spin symmetry. It turns out that they share a similar structure to the
form a triplet under the heavy-quark spin symmetry. It turns out that they share a similar structure to the  -mode of a singly heavy baryon as a result of the strongly attractive correlation for the doubly heavy diquark.
-mode of a singly heavy baryon as a result of the strongly attractive correlation for the doubly heavy diquark.
Ishikawa, Tsutomu*; Nakayama, Katsumasa*; Suzuki, Kei
Physical Review D, 104(9), p.094515_1 - 094515_11, 2021/11
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:37.94(Astronomy & Astrophysics)We investigate the Kondo effect with Wilson fermions. This is based on a mean-field approach for the chiral Gross-Neveu model including four-point interactions between a light Wilson fermion and a heavy fermion. For massless Wilson fermions, we demonstrate the appearance of the Kondo effect. We point out that there is a coexistence phase with both the light-fermion scalar condensate and Kondo condensate, and the critical chemical potentials of the scalar condensate are shifted by the Kondo effect. For negative-mass Wilson fermions, we find that the Kondo effect is favored near the parameter region realizing the Aoki phase. Our findings will be useful for understanding the roles of heavy impurities in Dirac semimetals, topological insulators, and lattice simulations.
Kim, Y.*; Liu, Y.-R.*; Oka, Makoto; Suzuki, Kei
Physical Review D, 104(5), p.054012_1 - 054012_18, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:74.69(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Chiral effective theory of scalar and vector diquarks is formulated according to the linear sigma model. The main application is to describe the ground and excited states of singly heavy baryons with a charm or bottom quark. Applying the potential quark model between the diquark and the heavy quark (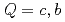 ), we construct a heavy-quark-diquark model. The spectra of the positive- and negative-parity states of
), we construct a heavy-quark-diquark model. The spectra of the positive- and negative-parity states of 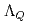 ,
, 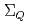 ,
, 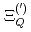 and
and 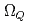 are obtained. The masses and interaction parameters of the effective theory are fixed partly from the lattice QCD data and also from fitting low-lying heavy baryon masses. We find that the negative parity excited states of
are obtained. The masses and interaction parameters of the effective theory are fixed partly from the lattice QCD data and also from fitting low-lying heavy baryon masses. We find that the negative parity excited states of 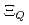 (flavor
(flavor 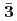 ) are different from those of
) are different from those of 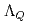 , because of the inverse hierarchy of the pseudoscalar diquark. On the other hand,
, because of the inverse hierarchy of the pseudoscalar diquark. On the other hand, 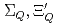 and
and 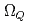 (flavor
(flavor 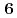 ) baryons have similar spectra. We compare our results of the heavy-quark-diquark model with experimental data as well as the quark model.
) baryons have similar spectra. We compare our results of the heavy-quark-diquark model with experimental data as well as the quark model.
Iwasaki, Sachio*; Jido, Daisuke*; Oka, Makoto; Suzuki, Kei
Physics Letters B, 820, p.136498_1 - 136498_6, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:18.91(Astronomy & Astrophysics)We investigate time evolution of  -wave charmonium populations under a time-dependent homogeneous magnetic field and evaluate survival probabilities of the low-lying charmonia to the goal of estimating the magnetic field strength at heavy-ion collisions. Our approach implements mixing between different spin eigenstates and transitions to radially excited states. We show that the survival probabilities can change even by an extremely short magnetic field. Furthermore, we find that the survival probabilities depend on the initial spin states. We propose the sum of the survival probabilities over spin partners as an observable insensitive to the initial states. We also find that the sum can be approximately given as a function of
-wave charmonium populations under a time-dependent homogeneous magnetic field and evaluate survival probabilities of the low-lying charmonia to the goal of estimating the magnetic field strength at heavy-ion collisions. Our approach implements mixing between different spin eigenstates and transitions to radially excited states. We show that the survival probabilities can change even by an extremely short magnetic field. Furthermore, we find that the survival probabilities depend on the initial spin states. We propose the sum of the survival probabilities over spin partners as an observable insensitive to the initial states. We also find that the sum can be approximately given as a function of 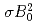 with a duration time
with a duration time  and the maximum strength of the magnetic field
and the maximum strength of the magnetic field 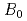 .
.
Iwasaki, Sachio*; Oka, Makoto; Suzuki, Kei
European Physical Journal A, 57(7), p.222_1 - 222_14, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:70.63(Physics, Nuclear)We review the properties of quarkonia under strong magnetic fields. The main phenomena are (i) mixing between different spin eigenstates, (ii) quark Landau levels and deformation of wave function, (iii) modification of 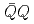 potential, and (iv) the motional Stark effect. For theoretical approaches, we review (i) constituent quark models, (ii) effective Lagrangians, (iii) QCD sum rules, and (iv) holographic approaches.
potential, and (iv) the motional Stark effect. For theoretical approaches, we review (i) constituent quark models, (ii) effective Lagrangians, (iii) QCD sum rules, and (iv) holographic approaches.
Araki, Yasufumi; Suenaga, Daiki*; Suzuki, Kei; Yasui, Shigehiro*
Physical Review Research (Internet), 3(2), p.023098_1 - 023098_17, 2021/05
Spins of relativistic fermions are related to their orbital degrees of freedom. In order to quantify the effect of hybridization between relativistic and nonrelativistic degrees of freedom on spin-orbit coupling, we focus on the spin-orbital (SO) crossed susceptibility arising from spin-orbit coupling. The SO crossed susceptibility is defined as the response function of their spin polarization to the "orbital" magnetic field, namely the effect of magnetic field on the orbital motion of particles as the vector potential. Once relativistic and nonrelativistic fermions are hybridized, their SO crossed susceptibility gets modified at the Fermi energy around the band hybridization point, leading to spin polarization of nonrelativistic fermions as well. These effects are enhanced under a dynamical magnetic field that violates thermal equilibrium, arising from the interband process permitted by the band hybridization. Its experimental realization is discussed for Dirac electrons in solids with slight breaking of crystalline symmetry or doping, and also for quark matter including dilute heavy quarks strongly hybridized with light quarks, arising in a relativistic heavy-ion collision process.
Suenaga, Daiki*; Araki, Yasufumi; Suzuki, Kei; Yasui, Shigehiro*
Physical Review D, 103(5), p.054041_1 - 054041_17, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:45.23(Astronomy & Astrophysics)We investigate the influence of the Kondo effect, namely, the nonperturbative effect induced by heavy impurities, on the chiral separation effect (CSE) in quark matter. We employ a simple effective model incorporating the Kondo condensate made of a light quark and a heavy quark, and compute the response function of the axial current to the magnetic field in the static and dynamical limits. As a result, we find that the Kondo effect catalyzes the CSE in both of the limits, and in particular the CSE in the dynamical limit can be enhanced by a factor of approximately 3. Our findings clearly show that the presence of heavy impurities in quark matter can play an important role in the transport phenomena of light quarks induced by a magnetic field.
Araki, Yasufumi; Suenaga, Daiki*; Suzuki, Kei; Yasui, Shigehiro*
Physical Review Research (Internet), 3(1), p.013233_1 - 013233_12, 2021/03
We investigate two different types of relativistic Kondo effects, distinguished by heavy-impurity degrees of freedom, by focusing on the energy-momentum dispersion relations of the ground state with condensates composed of a light Dirac fermion and a nonrelativistic impurity fermion. Heavy fermion degrees of freedom are introduced in terms of two types of heavy-fermion effective theories, in other words, two heavy-fermion limits for the heavy Dirac fermion, which is known as the heavy-quark effective theories (HQETs) in high-energy physics. While the first one includes only the heavy-particle component, the second one contains both the heavy-particle and heavy-antiparticle components, which are opposite in their parity. From these theories, we obtain two types of Kondo effects, in which the dispersions near the Fermi surface are very similar, but they differ in the structure at low momentum. We also classify the possible forms of condensates in the two limits. The two Kondo effects will be examined by experiments with Dirac/Weyl semimetals or quark matter, lattice simulations, and cold-atom simulations.
 *(2380)
*(2380)Kim, H.*; Kim, K. S.*; Oka, Makoto
Physical Review D, 102(7), p.074023_1 - 074023_10, 2020/10
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:70.16(Astronomy & Astrophysics)no abstracts in English
Takeuchi, Sachiko*; Giachino, A.*; Takizawa, Makoto*; Santopinto, E.*; Oka, Makoto
Hadron Spectroscopy and Structure; Proceedings of the 18th International Conference (HADRON 2019), p.333 - 337, 2020/08
Pentaquarks with 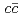 or
or 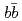 heavy quarks are very much interesting. We analyze the strange pentaquark with
heavy quarks are very much interesting. We analyze the strange pentaquark with 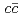 or
or 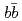 in the coupled-channel quark cluster model. We find bound, resonance and cusp like states.
in the coupled-channel quark cluster model. We find bound, resonance and cusp like states.
Kim, Y.*; Hiyama, Emiko*; Oka, Makoto; Suzuki, Kei
Physical Review D, 102(1), p.014004_1 - 014004_9, 2020/07
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:76.24(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Applying the chiral effective theory of diquarks, we analyze the spectrum and structure of singly heavy baryons. We introduce the phenomenological quark-model potentials for the confinement. We predict the charmed and bottom baryon spectrum showing the inverse mass hierarchy.
Suenaga, Daiki*; Suzuki, Kei; Araki, Yasufumi; Yasui, Shigehiro*
Physical Review Research (Internet), 2(2), p.023312_1 - 023312_13, 2020/06
The Kondo effect is induced by the interaction between light fermions near the Fermi surface and heavy impurities, and it affects electric/thermal/transport properties of matter. The chirality (right-handed or left-handed) is one of the unique properties of relativistic (Dirac or Weyl) fermions. In normal matter, the numbers of right- and left-handed particles are equivalent to each other, but environments with a chirality imbalance can also be realized. In this paper, we theoretically propose the Kondo effect driven by a chirality imbalance (or chiral chemical potential) of relativistic light fermions. This effect is caused by the mixing between a right-handed (or left-handed) fermion and a heavy impurity in the chirality imbalanced matter. This is different from the usual Kondo effect induced by finite density (or chemical potential) for light fermions. We construct an effective model with an interaction between a relativistic fermion and a heavy impurity, and we derive the realization of the Kondo effect from both a perturbative calculation and a nonperturbative mean-field approach. We also discuss the temperature dependence, the coupling constant dependence, the susceptibilities, and the order of the phase transition for the Kondo effect. Such a Kondo effect will be tested by future lattice simulations.
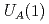 anomaly
anomalyHarada, Masayasu*; Liu, Y.-R.*; Oka, Makoto; Suzuki, Kei
Physical Review D, 101(5), p.054038_1 - 054038_11, 2020/03
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:74.34(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Using a chiral effective theory of diquarks, we analyze the spectrum and structure of diquark and heavy baryons consisting of diquarks. 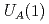 anomaly is considered in the chiral Lagrangian and its effects are studied.
anomaly is considered in the chiral Lagrangian and its effects are studied.
Giachino, A.*; Hosaka, Atsushi; Santopinto, E.*; Takeuchi, Sachiko*; Takizawa, Makoto*; Yamaguchi, Yasuhiro*
Recent Progress in Few-Body Physics; Springer Proceedings in Physics, Vol.238, p.621 - 627, 2020/01
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:94.26(Quantum Science & Technology)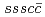 pentaquark states predicted by a quark model
pentaquark states predicted by a quark modelMeng, Q.*; Hiyama, Emiko*; Can, K. U.*; Gubler, P.; Oka, Makoto; Hosaka, Atsushi; Zong, H.*
Physics Letters B, 798, p.135028_1 - 135028_8, 2019/11
Times Cited Count:0